Dosing & Uses
Dosage Forms & Strengths
tablet
- 100mg
- 300mg
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Initial: 100 mg PO qDay taken before the first meal of the day
May increase dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerated in patients who have eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m² and require additional glycemic control
Indications
- Indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
- Also indicated to reduce risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI and stroke) in adults with T2DM and established cardiovascular disease
- Indicated to reduce the risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), doubling of serum creatinine, cardiovascular (CV) death, and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with T2DM and diabetic nephropathy with albuminuria ˃300 mg/day
Dosage Modifications
Renal impairment
- eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2: No dosage adjustment necessary
- eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2: 100 mg qDay
- eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 with albuminuria >300 mg/day: 100 mg qDay to reduce risk of end-stage kidney disease, doubling of serum creatinine, CV death, and hospitalization for heart failure
- eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2: Initiation not recommended
- On dialysis: Contraindicated
UGT enzyme inducers
-
eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2
- May increase canagliflozin dose to 200 mg qDay if currently tolerating 100 mg/day
- May increase canagliflozin dose to 300 mg qDay if currently tolerating 200 mg/day
-
eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2
- May increase canagliflozin dose to 200 mg qDay if currently tolerating 100 mg/day
- Consider adding another antihyperglycemic agent in patients who require additional glycemic control
Hepatic impairment
- Mild-to-moderate: No dosage adjustment is necessary
- Severe: Not studied and is therefore not recommended
Dosing Considerations
Not recommended for treating type 1 diabetes mellitus or diabetic ketoacidosis
Before initiating treatment
- Correct volume depletion
- Assess renal function and periodically thereafter
Safety and efficacy not established
Patients aged ≥65 years had a higher incidence of adverse reactions related to reduced intravascular volume (eg, hypotension, postural dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, syncope, dehydration), particularly with the 300 mg daily dose, compared with younger patients; a more prominent increase in the incidence was seen in patients who were ≥75 years
Smaller reductions in HbA1C compare to placebo were seen in older (≥65 years; -0.61% with 100-mg dose and -0.74% with 300-mg dose relative to placebo) compared with younger patients
Interactions
Interaction Checker
No Results

Contraindicated
Serious - Use Alternative
Significant - Monitor Closely
Minor

Contraindicated (0)
Serious - Use Alternative (0)
Monitor Closely (73)
- aliskiren
aliskiren and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- amiloride
amiloride and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- azilsartan
azilsartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- benazepril
benazepril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- betrixaban
canagliflozin increases levels of betrixaban by P-glycoprotein (MDR1) efflux transporter. Use Caution/Monitor. Decrease betrixaban dose to 80 mg PO once, then 40 mg PO qDay if coadministered with a P-gp inhibitor.
- candesartan
candesartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- captopril
captopril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor potassium
- carbamazepine
carbamazepine decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- chlorpropamide
chlorpropamide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- cyclosporine
cyclosporine and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- digoxin
canagliflozin increases levels of digoxin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Digoxin AUC and peak serum concentration increased when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- drospirenone
drospirenone and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- dulaglutide
dulaglutide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- enalapril
enalapril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eplerenone
eplerenone and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- eprosartan
eprosartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- finerenone
canagliflozin and finerenone both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Finerenone dose adjustment based on current serum potassium concentration. Monitor serum potassium and adjust finerenone dose as described in the prescribing information as necessary.
- fosinopril
fosinopril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- glimepiride
glimepiride, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- glipizide
glipizide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- glyburide
glyburide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- heparin
heparin and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- insulin aspart
insulin aspart, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin aspart. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - insulin aspart protamine/insulin aspart
canagliflozin, insulin aspart protamine/insulin aspart. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin degludec
canagliflozin, insulin degludec. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin degludec/insulin aspart
canagliflozin, insulin degludec/insulin aspart. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin detemir
insulin detemir, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin detemir. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - insulin glargine
insulin glargine, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin glargine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - insulin glulisine
insulin glulisine, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin glulisine. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - insulin inhaled
canagliflozin, insulin inhaled. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin isophane human/insulin regular human
canagliflozin, insulin isophane human/insulin regular human. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin lispro
insulin lispro, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin lispro. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - insulin lispro protamine/insulin lispro
canagliflozin, insulin lispro protamine/insulin lispro. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents.
- insulin NPH
insulin NPH, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin NPH. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - insulin regular human
insulin regular human, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
canagliflozin, insulin regular human. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Use Caution/Monitor. Antidiabetic agents are often used in combination; dosage adjustments may be required when initiating or discontinuing antidiabetic agents. - irbesartan
irbesartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- letermovir
letermovir will increase the level or effect of canagliflozin by unspecified interaction mechanism. Use Caution/Monitor. Monitor glucose concentrations.
- lisinopril
lisinopril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- lithium
canagliflozin decreases levels of lithium by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: SGLT2 inhibitors with lithium may decrease serum lithium concentrations; monitor serum lithium concentration more frequently during therapy initiation and dosage changes.
- lonapegsomatropin
lonapegsomatropin decreases effects of canagliflozin by Other (see comment). Use Caution/Monitor. Comment: Closely monitor blood glucose when treated with antidiabetic agents. Lonapegsomatropin may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Patients with diabetes mellitus may require adjustment of their doses of insulin and/or other antihyperglycemic agents.
lonapegsomatropin decreases effects of canagliflozin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone. - losartan
losartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- moexipril
moexipril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- nateglinide
nateglinide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- olmesartan
olmesartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- pentamidine
pentamidine and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- perindopril
perindopril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- phenobarbital
phenobarbital decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- phenytoin
phenytoin decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- potassium acid phosphate
potassium acid phosphate and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely.
- potassium chloride
potassium chloride and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- potassium citrate
potassium citrate and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- potassium citrate/citric acid
canagliflozin and potassium citrate/citric acid both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- potassium phosphates, IV
potassium phosphates, IV and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- quinapril
quinapril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- ramipril
ramipril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- repaglinide
repaglinide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- rifampin
rifampin decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- ritonavir
ritonavir decreases levels of canagliflozin by increasing metabolism. Use Caution/Monitor. Coadministration with potent UGT enzyme inducers: Consider increasing dose to 300 mg qDay if 100 mg/day tolerate and additional glycemic control required (eGFR must be >60 mL/min/1.73 m2 to increase dose); if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, consider using a different antihyperglycemic agent.
- sacubitril/valsartan
sacubitril/valsartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- somapacitan
somapacitan decreases effects of canagliflozin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone.
- somatrogon
somatrogon decreases effects of canagliflozin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone.
- somatropin
somatropin decreases effects of canagliflozin by pharmacodynamic antagonism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Growth hormone (GH) analogs may decrease insulin sensitivity, particularly at higher doses. Antidiabetic agents may require dose adjustment after initiating growth hormone.
- spironolactone
spironolactone and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- succinylcholine
succinylcholine and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tacrolimus
tacrolimus and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- telmisartan
telmisartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- tolazamide
tolazamide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- tolbutamide
tolbutamide, canagliflozin. Either increases effects of the other by pharmacodynamic synergism. Modify Therapy/Monitor Closely. Consider a lower dose of insulin or insulin secretagogue to avoid hypoglycemia when coadministered with canagliflozin.
- trandolapril
trandolapril and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- triamterene
triamterene and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- trimethoprim
trimethoprim and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- valsartan
valsartan and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
- voclosporin
voclosporin and canagliflozin both increase serum potassium. Use Caution/Monitor.
Minor (1)
- patiromer
patiromer, canagliflozin. cation binding in GI tract. Minor/Significance Unknown. No observed clinically important interaction. No separation of dosing required.
Adverse Effects
>10%
Female genital mycotic infections (10.4-11.4%)
1-10%
Urinary tract infections (4.4-5.9%)
Increased urination (4.6-5.1%)
Male genital mycotic infections (3.8-4.2%)
Thirst (2.4-2.8%)
Constipation (1.8-2.4%)
Nausea (2.1-2.3%)
Volume depletion
- Overall population (2.3-3.4%)
- Age >75 yr (4.9-8.7%)
- eGFR <60/mL/min/1.73 m³ (4.7-8.1%)
- Use of loop diuretic (3.2-8.8%)
Postmarketing reports
Ketoacidosis
Acute kidney injury
Anaphylaxis
Angioedema
Urosepsis
Pyelonephritis
Necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier’s gangrene)
Warnings
Contraindications
Serious hypersensitivity reaction (eg, anaphylaxis, angioedema)
Patients on dialysis
Cautions
Causes intravascular volume contraction and symptomatic hypotension and/or acute kidney injury can occur, particularly if eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, advance age, existing low systolic BP, or taking either diuretics or drugs that interfere with renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAS) (eg, ACE inhibitors, ARBs); monitor for signs and symptoms during therapy
Increases in serum creatinine and decreases in estimated GFR also observed with initiation
Increases risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs), including life-threatening urosepsis and pyelonephritis that started as UTIs; evaluate patients for signs and symptoms of urinary tract infections and treat promptly, if indicated
Necrotizing fasciitis of the perineum (Fournier gangrene) reported with SGLT2 inhibitors; signs and symptoms include tenderness, redness, or swelling of the genitals or the area from the genitals back to the rectum, and have a fever >100.4ºF or a general feeling of being unwell; if suspected, discontinue SGLT2 inhibitor and start treatment immediately with broad-spectrum antibiotics and surgical debridement if necessary
Genital mycotic infections may occur, patients with history of genital mycotic infections and uncircumcised males are more susceptible
Increased risk of bone fracture, occurring as early as 12 weeks after treatment initiation, reported; consider factors that contribute to fracture risk before initiating therapy
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and anaphylaxis reported; reactions generally occurred within hours to days after initiation; if hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue therapy; treat and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve
Lower limb amputation
- Increased risk of lower limb amputations associated with canagliflozin use was observed in 2 large, randomized, placebo-controlled trials (CANVAS AND CANVAS-R) in patients with type 2 diabetes who had established cardiovascular disease (CVD) or were at risk for CVD
- Amputations of the toe and midfoot were most frequent; however, amputations involving the leg were also observed; some patients had multiple amputations, some involving both limbs
- Before initiating, consider factors that may increase the risk of amputation (eg, history of prior amputation, peripheral vascular disease, neuropathy, diabetic foot ulcers)
- Monitor for infection, new pain or tenderness, and sores or ulcers involving the lower limbs; discontinue if these complications occur
Ketoacidosis
- Ketoacidosis associated with SGLT2 inhibitors reported; monitor for signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis (eg, difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, unusual fatigue or sleepiness)
- Before initiating therapy, consider factors in patient history that may predispose to ketoacidosis, including pancreatic insulin deficiency from any cause, caloric restriction, and alcohol abuse
- Consider temporarily discontinuing canagliflozin for at least 3 days before undergoing scheduled surgery to avoid euglycemic ketoacidosis
- Consider monitoring for ketoacidosis and temporarily discontinuing therapy in other clinical situations known to predispose to ketoacidosis (eg, prolonged fasting due to acute illness or post-surgery)
- Restart once the patient’s oral intake is back to baseline and any other risk factors for ketoacidosis (blood acid buildup) are resolved
Diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- In patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, this drug significantly increases risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a life-threatening event, beyond the background rate; this risk may be greater with higher doses of the drug; This therapy is not indicated for glycemic control in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus and pancreatic disorders (eg, history of pancreatitis or pancreatic surgery) are also risk factors for ketoacidosis; there have been postmarketing reports of fatal events of ketoacidosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using SGLT2 inhibitors, including this medication
- Precipitating conditions for diabetic ketoacidosis or other ketoacidosis include acute febrile illness, reduced caloric intake, ketogenic diet, surgery, insulin dose reduction, volume depletion, and alcohol abuse
- Signs and symptoms are consistent with dehydration and severe metabolic acidosis and include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, generalized malaise, and shortness of breath; blood glucose levels at presentation may be below those typically expected for diabetic ketoacidosis (eg, less than 250 mg/dL)
- Ketoacidosis and glucosuria may persist longer than typically expected; urinary glucose excretion persists for 3 days after discontinuing therapy; however, there have been postmarketing reports of ketoacidosis and glucosuria lasting greater than 6 days and some up to 2 weeks after discontinuation of SGLT2 inhibitors
- Consider ketone monitoring in patients at risk for ketoacidosis if indicated by clinical situation; assess for ketoacidosis regardless of presenting blood glucose levels in patients who present with signs and symptoms consistent with severe metabolic acidosis
- If ketoacidosis is suspected, discontinue therapy, promptly evaluate, and treat ketoacidosis, if confirmed; monitor patients for resolution of ketoacidosis before restarting therapy
- Withhold therapy, if possible, in temporary clinical situations that could predispose patients to ketoacidosis; resume therapy when patient is clinically stable and has resumed oral intake
- Educate all patients on signs and symptoms of ketoacidosis and instruct patients to discontinue therapy and seek medical attention immediately if signs and symptoms occur
Drug interaction overview
- Major substrate of UGT1A9 and UGT2B4; weak inhibitor of P-gp
- Coadministration of canagliflozin with rifampin, a nonselective inducer of several UGT enzymes, including UGT1A9, UGT2B4, decreased canagliflozin AUC by 51%
- Hypoglycemia risk increased with insulin and insulin secretagogues, consider a lower dose of insulin or the insulin secretagogue
- An increase in AUC and mean peak drug concentration of digoxin (a P-gp substrate) was observed when coadministered with canagliflozin 300 mg; monitor
Laboratory testing
- Urine glucose tests is not recommended in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors as SGLT2 inhibitors increase urinary glucose excretion and will lead to positive urine glucose tests; use alternative methods to monitor glycemic control
- 1,5-AG assay is not recommended as measurements of 1,5- AG are unreliable in assessing glycemic control in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors; use alternative methods to monitor glycemic control
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Based on animal data showing adverse renal effects, not recommended during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy
Data are limited in pregnant women and are not sufficient to determine a drug associated risk for major birth defects or miscarriage
Clinical considerations
- Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, preeclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, stillbirth, and delivery complications
- Poorly controlled diabetes increases fetal risk for major birth defects, stillbirth, and macrosomia related morbidity
Lactation
No information regarding distribution in human milk or effects on the breastfed infant or milk production
Present in milk of lactating rats
Since human kidney maturation occurs in utero and during the first 2 yr of life when lactational exposure may occur, there may be risk to the developing human kidney
Inform women not to breastfeed while taking canagliflozin
Pregnancy Categories
A: Generally acceptable. Controlled studies in pregnant women show no evidence of fetal risk.
B: May be acceptable. Either animal studies show no risk but human studies not available or animal studies showed minor risks and human studies done and showed no risk. C: Use with caution if benefits outweigh risks. Animal studies show risk and human studies not available or neither animal nor human studies done. D: Use in LIFE-THREATENING emergencies when no safer drug available. Positive evidence of human fetal risk. X: Do not use in pregnancy. Risks involved outweigh potential benefits. Safer alternatives exist. NA: Information not available.Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Selective sodium-glucose transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitor
SGLT-2 inhibition lowers the renal glucose threshold (ie, the plasma glucose concentration which exceed the maximum glucose reabsorption capacity of the kidney); lowering the renal glucose threshold results in increased urinary glucose excretion
Absorption
Bioavailability: 65%
Peak plasma time: 1-2 hr
Distribution
Protein bound: 99% (predominantly to albumin)
Vd: 119 L
Metabolism
O-glucuronidation is the major metabolic elimination pathway, mainly by UGT1A9 and UGT2B4 to 2 inactive O-glucuronide metabolites
CYP3A4-mediated (oxidative) metabolism is minimal (~7%)
Elimination
Half-life: 10.6 hr (100 mg dose); 13.1 hr (300 mg dose)
Total body clearance: 192 mL/min
Excretion
- Feces: 41.5% (canagliflozin), 7% (hydroxylated metabolite), 3.2% (O-glucuronide metabolite)
- Urine: 33% excreted in urine, mainly as O-glucuronide metabolites (30.5%); <1% excreted unchanged
Administration
Oral Administration
Take orally with or without food
Missed dose
- If dose missed, take as soon as possible
- If it is almost time for next dose, skip missed dose and administer next scheduled dose
- Do not to take 2 doses at the same time
Storage
Capsules: Store at 20-25ºC (68-77ºF); excursions permitted between 15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
Images
| BRAND | FORM. | UNIT PRICE | PILL IMAGE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invokana oral - | 100 mg tablet | 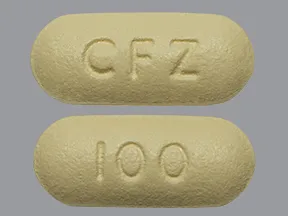 | |
| Invokana oral - | 300 mg tablet |  |
Copyright © 2010 First DataBank, Inc.
Formulary
Adding plans allows you to compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
To view formulary information first create a list of plans. Your list will be saved and can be edited at any time.
Adding plans allows you to:
- View the formulary and any restrictions for each plan.
- Manage and view all your plans together – even plans in different states.
- Compare formulary status to other drugs in the same class.
- Access your plan list on any device – mobile or desktop.






